Introduction
In the realm of facility management, the integration of advanced technologies into maintenance practices has become a cornerstone for operational efficiency. One such technology is infrared inspections, which play a critical role in predictive maintenance programs. This article delves into the significance of integrating infrared inspections into predictive maintenance strategies, focusing on their impact on cost-effective facility management.
Overview of Predictive Maintenance
Predictive maintenance is a proactive approach that utilizes data analysis to predict equipment failures before they occur. By employing various technologies, including sensors and software, facility managers can assess the condition of machinery and systems. This approach contrasts sharply with traditional maintenance methods, which often rely on scheduled or reactive maintenance, leading to unnecessary downtime and increased operational costs.
Introduction to Infrared Inspections
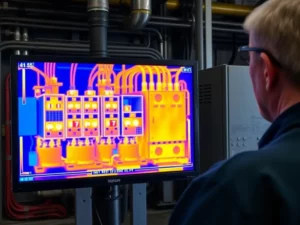
Infrared inspections leverage thermal imaging technology to detect temperature variations in equipment and systems. These temperature differences can indicate issues such as electrical malfunctions, mechanical wear, or insulation problems. By identifying these issues early, facility managers can take corrective action before they escalate, minimizing downtime and repair costs.
Significance of Cost-Effective Facility Management
Effective facility management hinges on maximizing operational efficiency while minimizing costs. Integrating advanced inspection technologies like infrared inspections not only enhances the reliability of systems but also leads to significant cost savings. For business owners and facility managers, understanding the value of these inspections is essential for maintaining a competitive edge.
Understanding Infrared Inspections
What Are Infrared Inspections?
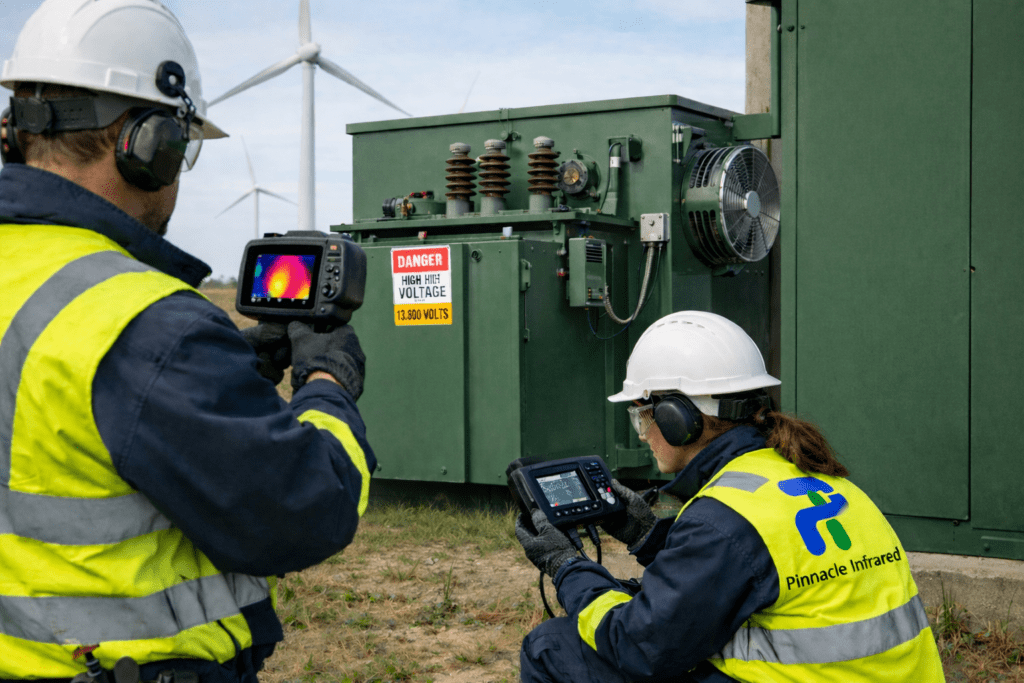
Infrared inspections involve using thermal imaging cameras to capture the heat emitted from objects. This technology allows for a non-invasive examination of electrical systems, mechanical equipment, and building envelopes. By translating thermal radiation into visual images, infrared inspections provide a clear indication of temperature anomalies that could signify potential failures.
How Infrared Technology Works
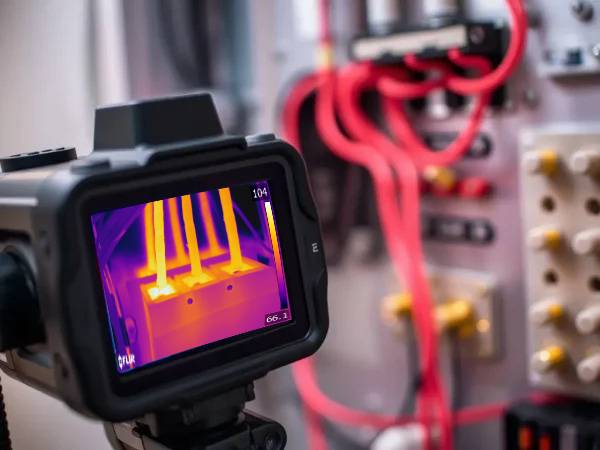
The fundamental principle behind infrared technology is that all objects emit thermal energy. Infrared cameras detect this radiation and convert it into thermal images, highlighting areas of high and low temperature. When integrated into a predictive maintenance program, these inspections enable facility managers to monitor equipment continuously and assess the thermal performance of systems.
Common Applications in Facility Management
Infrared inspections have numerous applications in facility management. They are commonly used for electrical inspections to identify overloaded circuits, loose connections, or faulty components. Additionally, they help in evaluating mechanical systems for lubrication failures, misalignments, or overheating. Infrared technology is also effective in assessing building envelopes to spot insulation deficiencies, moisture intrusion, and air leaks.
Benefits of Integrating Infrared Inspections
Early Detection of Issues
One of the primary benefits of integrating infrared inspections into predictive maintenance is the ability to detect issues before they become critical. By regularly monitoring equipment, facility managers can identify potential problems—such as overheating motors or electrical connections—early enough to schedule repairs, thereby avoiding costly emergency interventions.
Reduction of Downtime
Downtime can be detrimental to any facility’s productivity and profitability. Implementing infrared inspections allows for predictive insights that facilitate timely maintenance actions, which can significantly reduce unplanned outages. By addressing potential failures before they occur, businesses can maintain operational continuity and enhance overall efficiency.
Improved Energy Efficiency
Infrared inspections can also lead to improved energy efficiency. By identifying thermal leaks and insulation issues, facility managers can make informed decisions to enhance energy performance. This not only contributes to lower utility costs but also supports sustainability initiatives, making the facility more environmentally friendly.
Cost Savings and ROI
The financial implications of integrating infrared inspections into predictive maintenance programs are substantial. By preventing equipment failures and reducing downtime, businesses can save significantly on repair and replacement costs. Furthermore, the enhanced energy efficiency translates to lower operating expenses. The return on investment (ROI) for implementing infrared inspections can be realized quickly, making it a financially sound strategy for facility management.
Case Studies Demonstrating Effectiveness
Case Study 1: Manufacturing Facility
A manufacturing facility implemented infrared inspections as part of its predictive maintenance strategy. By regularly monitoring electrical panels and motors, the facility identified several overheating components that could have led to catastrophic failures. As a result, they were able to repair these components proactively, reducing downtime by 40% and saving thousands in potential repair costs.
Case Study 2: Commercial Building
In a large commercial building, infrared inspections were used to evaluate the HVAC system. The inspections revealed significant insulation issues, leading to excessive energy consumption. By addressing these issues, the facility improved its energy efficiency by 25%, resulting in annual savings of over $20,000 on energy bills.
Case Study 3: Data Center
A data center integrated infrared inspections to monitor critical equipment. The early detection of heat anomalies in server racks allowed the facility to balance loads and optimize cooling systems effectively. This not only prevented potential failures but also extended the life of the equipment, yielding a substantial ROI through enhanced operational reliability.
Implementing Infrared Inspections in Predictive Maintenance Programs
Steps for Integration
To successfully integrate infrared inspections into predictive maintenance programs, facility managers should follow a systematic approach. First, they should assess their current maintenance practices and identify areas where infrared inspections can provide value. Next, they need to develop a clear plan that includes scheduling inspections, selecting appropriate equipment, and defining objectives for the inspections.
Choosing the Right Technology and Equipment
The selection of appropriate infrared technology and equipment is crucial for effective inspections. Facility managers should invest in high-quality thermal imaging cameras that offer advanced features such as high resolution and sensitivity. Additionally, they should consider software solutions that can analyze thermal data and generate comprehensive reports, aiding in decision-making processes.
Training and Development for Staff
Proper training is a vital component of implementing infrared inspections. Staff members conducting the inspections must be well-trained in using thermal imaging technology and interpreting thermal images. Training programs should also cover the significance of infrared inspections within the broader context of predictive maintenance, ensuring that all team members understand their role in maintaining equipment health.
Challenges and Solutions
Common Challenges in Integration
Despite the clear benefits, integrating infrared inspections into predictive maintenance programs can present challenges. Common obstacles include resistance to change among staff, lack of understanding of the technology, and budget constraints. Additionally, some facilities may struggle with scheduling inspections and ensuring consistent monitoring.
Solutions and Best Practices
To overcome these challenges, facility managers should foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation. Communicating the benefits of infrared inspections to staff can help mitigate resistance to change. Furthermore, allocating a budget for training and technology acquisition is essential. Best practices include establishing a regular inspection schedule, utilizing software for data management, and continuously evaluating the effectiveness of the infrared inspections.
Conclusion
Summary of Key Points
Integrating infrared inspections into predictive maintenance programs offers numerous benefits, including early detection of issues, reduced downtime, improved energy efficiency, and significant cost savings. Case studies demonstrate the effectiveness of this approach, highlighting successful implementations across various facility types.
The Future of Infrared Inspections in Facility Management
As technology continues to evolve, the role of infrared inspections within predictive maintenance programs is likely to expand. The adoption of artificial intelligence and machine learning can enhance data analysis and predictive capabilities, further improving maintenance practices. Facility managers who embrace these advancements will be better positioned to optimize their operations and achieve cost-effective facility management.
FAQs
What is infrared inspection?
Infrared inspection is a non-invasive technique that uses thermal imaging to identify temperature differences in equipment and systems, helping to detect potential failures.
How often should infrared inspections be conducted?
The frequency of infrared inspections depends on the equipment and systems in place, but many facilities benefit from inspections at least once a year or more frequently for critical systems.
What equipment is needed for infrared inspections?
Essential equipment includes a thermal imaging camera, software for data analysis, and safety gear for personnel conducting the inspections.
Can infrared inspections save money?
Yes, by preventing equipment failures, reducing downtime, and improving energy efficiency, infrared inspections can lead to significant cost savings over time.
Is training necessary for infrared inspections?
Yes, proper training is crucial for personnel to effectively use thermal imaging technology and interpret the results accurately.